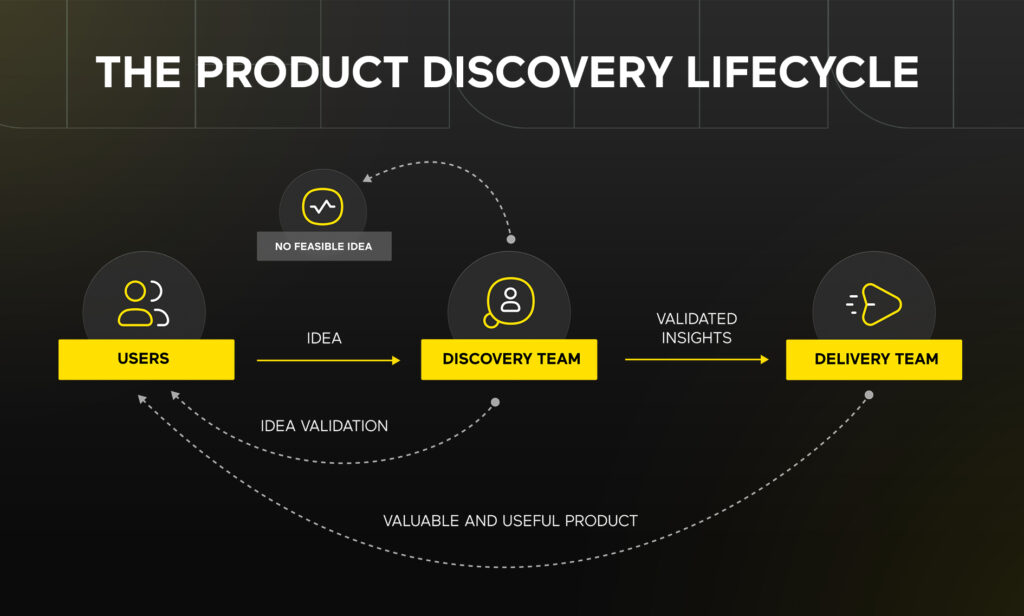
Product Discovery Checklist
- Set up product discovery team
- Establish Team Communication Cadence
- Research the Discovery Topic
- Conduct User Research
- Identify Common Problems
- Prioritize Opportunities
- Brainstorm Possible Solutions
- Validate Product and Feature Ideas
- Create and Test Prototypes Before Development
- Get Aligned with Stakeholders
1. Set up product discovery team
To kick things off, you must start with a strong and diverse foundation. That entails not only recruiting a talented product discovery team, but also fostering a positive work agile discovery phase that encourages teams to take responsibility for achieving desired results.
By assembling a team with members from various backgrounds and areas of expertise, the product discovery team can build a discovery checklist and analyze the set of product requirements and needs competently. This enables them to make informed decisions and develop solutions that are both practical and aligned with research findings. The discovery team members should collaborate to establish the product requirements and carry out the required research. Cross-functional collaboration between product, design, and engineering team members is key to ensuring technical viability and user focus.
The product discovery team normally consists of:
- Product Owner (PO) (role can be fulfilled by Business Analyst (BA) and/or Product Manager (PM))
- UX/UI Designer
- Solution Architect
- Software Engineering Lead
- SMEs (Subject-Matter Experts)
- Project Manager (PM)
It is also important to involve stakeholders from business and marketing into the product discovery process in agile to gain a comprehensive understanding of the product, user base, and business targets.
Once you have identified your product discovery leaders, determine who will be part of the second tier. These individuals will be kept informed about the progress of the Agile discovery session and will be involved in collaboration during specific stages. This group usually includes marketers or sales representatives, developers, and other team members.
Typically, the Product Owner, along with subject-matter experts (SMEs), will define the “What,” “When,” and “Why” aspects, while the Solution Architect and Engineers will focus on defining the “How.” SMEs can extend beyond just technological experts.

2. Establish Team Communication Cadence
After defining the product discovery team, it is important to develop agile discovery sessions and schedule future communication time slots for the team members and stakeholders. These sessions can include a product discovery kick-off meeting, vision and scope elicitation meetings, design sessions, and technical calls.
A kick-off session is scheduled to align the team on the discovery plan and next steps. This session includes team introductions, agreement on roles and ways of working for the discovery phase, as well as a review of the discovery scope and deliverables.
If the agile discovery phase involves creating a clickable prototype or mockups, the Designer schedules UX/UI sessions to start sketching out the potential appearance of the solution.
Technical sessions are conducted to review the technical landscape and collaborate on mapping out the future solution.
The discovery checklist or “scope elicitation sessions”, as they are sometimes called, during product discovery in agile are essential as they form the core of the discovery process. These sessions involve gathering requirements and expectations from stakeholders, defining the boundaries and objectives of the project, and determining the product scope.
Regular communication with stakeholders allows the Agile product team to showcase the current progress of the discovery phase, ensure that the team is on the right track, and make any necessary updates before the end of discovery.
At the end of the Discovery phase, it is important to present the outcomes of the completed discovery weeks to a wider group of stakeholders during a Discovery wrap-up session. This session provides an opportunity to finalize the scope, summarize the discovery process, and discuss the next steps for the possible delivery stage.
3. Research the Discovery Topic
During the early stage of Product Discovery, it is important to conduct thorough research on the chosen topic. This research process includes several main elements that contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Establishing strong alignment with stakeholders is essential to gain a clear understanding of their needs and expectations.
Conducting market research is vital to identify trends and opportunities. Market research involves analyzing market dynamics, studying competitors, and identifying potential gaps or areas for innovation. By gaining insights into the market landscape, the discovery team can make informed decisions and develop a product that stands out in the industry.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of competitors is a key aspect of the discovery phase. By analyzing the competition, the team can identify areas where they can differentiate their product and gain a competitive advantage. This research helps shape the product strategy and effectively position it in the market.
By understanding the unique needs and preferences of the target audience, a product can be developed and tailored to provide the utmost satisfaction and value to its users. This not only enhances the overall user experience but also increases the chances of the product gaining widespread acceptance and achieving its desired goals.
4. Conduct User Research
A common pitfall in product discovery is rushing into the solution space without fully understanding your customers’ problems. So the most important discovery rule is simple: “Communicate first with your users”. As product discovery expert Teresa Torres (ProductTalk founder) says, “Customers know more than we’ll ever know about their needs and context.”
One of the primary goals of the discovery phase is to gain a comprehensive understanding of users’ needs. This involves conducting research, collecting feedback, and analyzing data to identify areas of concern and potential opportunities. By doing so, the discovery team can ensure that the final product is tailored to meet the specific needs and preferences of its target audience.
Some ways to conduct product research are:
- Customer feedback surveys
- Customer interviews
- Focus groups
- Product usage analysis
- User behavior data
We need to engage in conversations with customers to learn about their roles and the tasks they need to accomplish. This information can later be used to build Jobs To Be Done (JTBD). User research helps to discover their identities and create user and product personas, which vividly represent their demographics and foster a strong sense of user empathy.
To build empathy, you should not only understand customers but also ensure that the individuals we are empathizing with come from a diverse range of demographics. Otherwise, you may create a biased and non-representative sample, which could prevent you from earning their trust.
The customer-centric approach ensures that the final product is tailored to meet the specific needs of the target audience, resulting in a better user experience.
To gain a better understanding of your audience, it is important to be specific. Identify your ideal target customer and learn everything about them, including their occupation, income, interests, and desires. Additionally, make note of any potential issues they may face in their lives and align your offerings with what your customers love, hate, want, and already have.
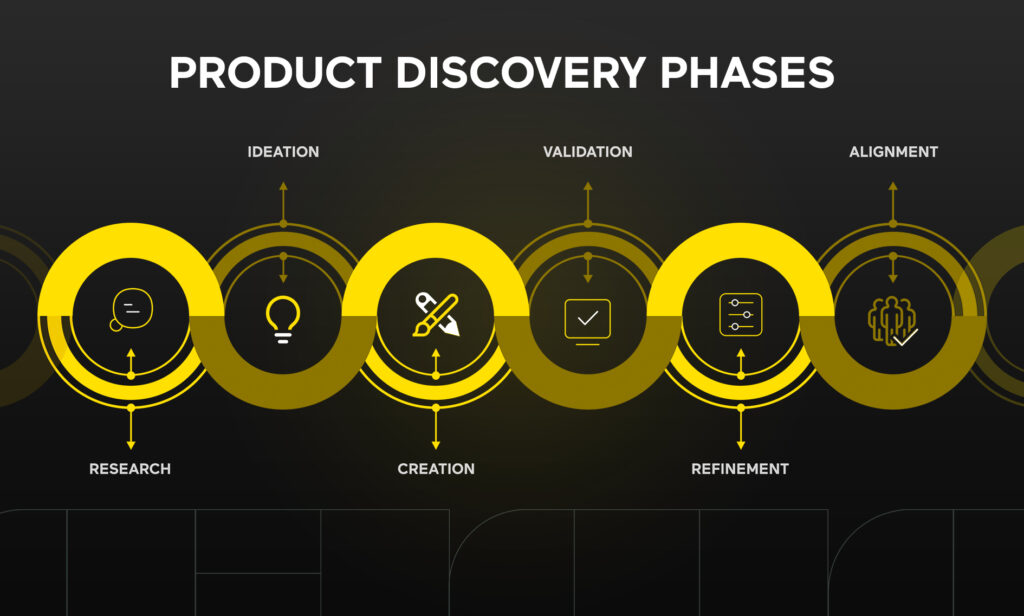
5. Identify Common Problems
Once user data has been gathered and research conducted, the next step is to analyze the data and identify common patterns. This involves recognizing recurring user problems, needs, or desires from various users and sources. By doing so, the team can pinpoint the most significant user problems and use them to generate discovery questions and hypotheses. This step is needed for prioritizing opportunities and addressing the most urgent user problems.
The main goal of this step is to find ways to enhance the product and provide a more satisfying user experience. These opportunities may include identifying user issues, requirements, or preferences.
Now that you have collected user data, you should dedicate time to thoroughly analyze it and convert the data into actionable insights. Start by creating a map of user stories to identify patterns or recurring topics from various users and sources. Then, refine these topics into key user problems and use them to generate broad and specific discovery questions and hypotheses.
6. Prioritize Opportunities
To successfully launch a product, the team should be efficient and adaptable. Slow progress will not lead to success. It can be quite daunting to move at a fast pace, especially for individuals who are not familiar with the intricacies of starting a company. However, it is important to remember that your dreams are on the line, and rushing without careful consideration can lead to costly mistakes.
One of the key aspects of a successful product launch is prioritizing opportunities based on their alignment with the product vision and business objectives. Product teams often dedicate a substantial amount of time to using various frameworks, such as the Kano Model, ICE or RICE Scoring, or Buy-a-Feature, to effectively prioritize opportunities. By employing these frameworks, the team can concentrate on addressing the most significant user problems, thus ensuring that the final product delivers an exceptional user experience.
It is worth noting that not all opportunities will align with the product vision. In such cases, utilizing an Opportunity Solution Tree (OST) can prove to be immensely helpful. This tool allows the team to visually map out user pain points and needs, facilitating the determination of how they align with business objectives.
Even after meticulously following this process, there may still be a myriad of problems that require attention, surpassing the team’s capacity to address them all.
7. Brainstorm Possible Solutions
Once you have identified the most optimal opportunities, it is time to explore the solution space in more depth and generate a wide range of ideas. Keep in mind that the discovery process is a collaborative effort that requires active participation from all stakeholders. By involving everyone, you can leverage their diverse expertise and unique perspectives, which in turn leads to the emergence of more innovative ideas, a more accurate assessment of feasibility, and a stronger sense of ownership.
During brainstorming sessions, it is useful to create an environment that fosters creativity and encourages thinking outside the box. Consider using techniques such as mind mapping and story boarding to stimulate the team’s creativity. It’s worth noting that even seemingly impractical ideas can serve as valuable sources of inspiration and insights, which can be refined and further developed later on.
To encourage innovation from different angles, it is recommended to involve as many cross-functional roles as possible in the brainstorming process. This ensures a comprehensive approach and diverse perspectives that can contribute to the generation of truly groundbreaking ideas.
Once the team has generated a significant number of ideas, it may be helpful to utilize a voting system to narrow down the shortlist of ideas. This can streamline the decision-making process and determine which ideas should be further validated and pursued.

8. Validate Product and Feature Ideas
In product discovery, the ultimate goal is validation. Validating ideas helps determine which ideas to pursue and prioritize the most essential initiatives. When brainstorming product or feature ideas, it’s important to continuously validate them without investing excessive time or money. Techniques like fake door testing can be used, where a link to a non-existent product or feature is created on the webpage, and user interest is tracked based on clicks. Additionally, incoming feedback widgets can be used to ask users why they clicked on the link.
Validating ideas with current or potential users is critical. This can be done through user interviews, surveys, or A/B testing to compare different solutions. Analyzing heatmaps can provide insights into user clicks and engagement.
Internal validation of ideas may involve consulting with stakeholders to assess usability, feasibility, and technical solutions. Opportunity mapping, such as using a value curve to compare your solution to the market, can also help determine if your solution aligns with business goals.
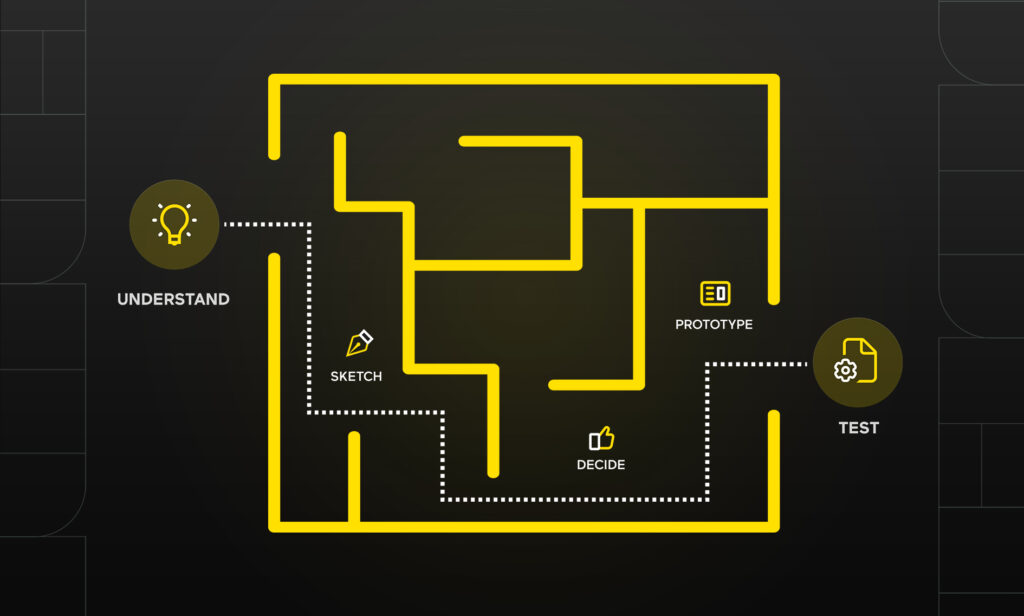
Solution validation is another critical component of the discovery phase and should be performed before development begins. It helps ensure that the final product is effective and meets users’ needs. There are various ways to validate solutions, including creating prototypes, conducting usability testing, and gathering feedback from stakeholders.
9. Create and Test Prototypes Before Development
Prototype testing is an iterative process that involves creating initial simple prototypes, such as wireframes, and gathering customer feedback to improve and develop more detailed prototypes.
As the process continues, the initial product idea evolves into a fully functional Minimum Viable Product (MVP). Thus, prototype testing marks the beginning of the product delivery process.
To ensure consistency between users’ responses to a product idea and their actual product experience, it is important to test it using mockups and prototypes.
For instance, if users express a desire for new video editing features on the dashboard of a subtitling software, implementing those features may clutter their view and hinder their overall product experience. This can only be identified through testing.
There are various methods to conduct this testing, such as creating mockups or clickable prototypes, or observing users as they interact with similar products to identify what does and doesn’t address their problems. The objective is to develop an MVP that can be further tested.
10. Get Aligned with Stakeholders
Once you have thoroughly tested potential solutions, it is time to present them to various stakeholders. This step is vital as it allows you to gather feedback and insights from different perspectives. By following all the above steps, you should have a comprehensive understanding of user needs and responses, which will serve as a strong foundation for your proposals.
To gain stakeholder buy-in and support, it is important to provide a wide range of data. Quantitative data, such as statistics and metrics, can demonstrate the impact and effectiveness of your ideas in terms of user satisfaction and overall business objectives. Additionally, incorporating qualitative data, such as Voice of the Customer (VoC) insights, customer quotes, and user feedback, can further strengthen your arguments and make them more persuasive.
To effectively convey your message and capture the attention of stakeholders, consider using techniques like product storytelling and conducting stakeholder analysis. By crafting a compelling narrative around your proposals and understanding the specific needs and interests of each stakeholder, you can tailor your communication approach and increase the likelihood of gaining their support and approval.
Conclusion
The discovery phase sets the tone for the entire project, ensuring its success by demonstrating how the product will work, what it will look like, and how it will help your business achieve its goals. It acts as a guide that directs the project towards its ultimate destination. From defining a clear goal to prioritizing opportunities, each step in the discovery phase is key to successful product development, ensuring that the final product meets user needs and provides a great user experience.
By following this product discovery checklist, product owners and their Agile teams can effectively manage a comprehensive product discovery process, enabling them to gain a deep understanding of their customers. However, each product team has its unique approach to work. Some teams may focus on delivering one feature or set of features before moving on to the next, while others may have different team members responsible for different stages of the product discovery and development journey.
While it is useful to break down product discovery as a step-by-step, linear chronological process, in practice, it doesn’t have to come to an end. A digital product is never truly complete. Therefore, it is important to continuously collect feedback from the customers to ensure that we are developing the right features and functionalities.



